Table of Contents
Understanding Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing
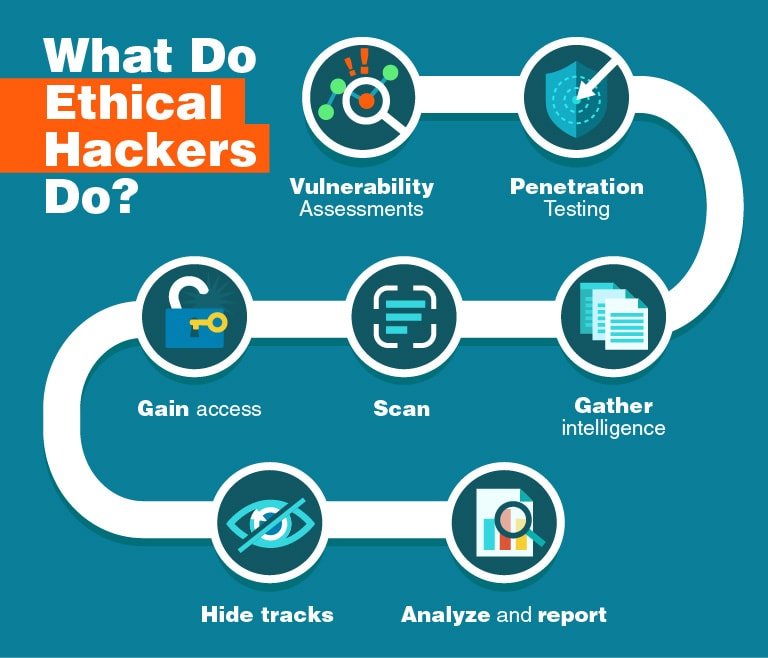
In today’s digitally driven world, ensuring the security of sensitive information and systems is paramount. Ethical hacking, also known as penetration testing, is a proactive approach employed by organizations to identify and rectify vulnerabilities in their IT infrastructure before malicious actors exploit them. However, conducting ethical hacking requires meticulous planning, adherence to ethical standards, and a deep understanding of cybersecurity principles.
Obtain Prior Approval
Before embarking on any penetration testing endeavor, it is imperative to obtain explicit authorization from the organization or individual who owns the IT assets. This step ensures that the testing activities are conducted within legal and ethical boundaries, preventing any unintended repercussions.
Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Familiarize yourself with the legal and regulatory frameworks governing penetration testing in your jurisdiction. This includes understanding laws related to unauthorized access to computer systems, data privacy regulations, and intellectual property rights.
Document Authorization
Obtain written consent or formal approval from the organization’s management, clearly outlining the scope, objectives, and limitations of the penetration testing exercise.

Utilize Automated and Manual Techniques
To uncover vulnerabilities comprehensively, it is essential to employ a combination of automated scanning tools and manual testing methodologies.
Automated Scanning
Utilize automated scanning tools to identify common vulnerabilities such as misconfigurations, outdated software, and known security loopholes. These tools can efficiently scan large networks and systems, providing a preliminary assessment of potential weaknesses.
Manual Testing
Supplement automated scans with manual testing techniques to uncover complex vulnerabilities that may evade detection by automated tools. Manual testing involves thorough analysis, reverse engineering, and exploitation of system weaknesses by experienced ethical hackers.
Prepare for the Test
Effective preparation is key to conducting a successful penetration test without disrupting critical business operations or causing unintended damage to IT systems.
Understand Testing Constraints
Familiarize yourself with the constraints imposed by your hosting or cloud service provider, such as permissible testing methods, blackout periods, and restrictions on testing certain systems.
Establish Communication Channels
Establish clear communication channels between your testing team, organizational stakeholders, and any external service providers involved in the testing process. This ensures seamless coordination and prompt resolution of any issues that may arise during testing.
Choose a Qualified Penetration Tester
Selecting a qualified and reputable penetration testing service provider is crucial for ensuring the effectiveness and integrity of the testing process.
Assess Expertise and Credentials
Evaluate the expertise, experience, and certifications of potential penetration testing providers. Look for professionals who possess certifications such as Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP), or Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP).
Verify Methodologies and Standards
Ensure that the chosen penetration testing provider follows recognized methodologies and standards, such as the Penetration Testing Execution Standard (PTES), OWASP Web Security Testing Guide, or NIST Special Publication 800-115.
Conduct Regular Meetings
Maintaining open lines of communication and regular progress updates is essential throughout the penetration testing process.
Schedule Progress Meetings
Schedule regular meetings with key stakeholders to discuss testing progress, address any concerns or questions, and share important findings or insights.
Foster Collaboration
Encourage collaboration and knowledge sharing between the testing team, IT personnel, and other relevant stakeholders to ensure a holistic approach to security testing.
Use Hacking Tools Safely
While ethical hackers utilize various tools and techniques to identify vulnerabilities, it is essential to use these tools responsibly and legally.
Obtain Proper Authorization
Ensure that you have explicit permission from the organization or system owner before using any hacking tools or conducting intrusive testing activities.
Exercise Caution
Exercise caution when using hacking tools to avoid unintended damage or disruption to IT systems. Familiarize yourself with the capabilities and limitations of each tool to minimize the risk of false positives or false negatives.
Follow Ethical Hacking Standards
Adhering to established ethical hacking standards and best practices is fundamental to maintaining the integrity and credibility of penetration testing activities.
Adhere to Codes of Conduct
Abide by ethical codes of conduct, such as the EC-Council’s Code of Ethics for Certified Ethical Hackers, which emphasizes integrity, confidentiality, and respect for legal boundaries.
Stay Informed
Stay abreast of emerging cybersecurity threats, vulnerabilities, and mitigation strategies by participating in relevant training programs, conferences, and industry forums.
Report and Remediate
Effective communication of testing results and timely remediation of identified vulnerabilities are essential components of a successful penetration testing initiative.
Prepare Detailed Reports
Generate comprehensive reports detailing the findings of the penetration test, including identified vulnerabilities, exploitation techniques, and recommendations for remediation.
Collaborate on Remediation Efforts
Collaborate closely with organizational stakeholders to prioritize and address identified vulnerabilities promptly. Develop and implement robust remediation plans to mitigate security risks effectively.
Conclusion
Performing ethical hacking safely for penetration testing requires meticulous planning, adherence to ethical standards, and collaboration between stakeholders. By following best practices, utilizing appropriate tools and techniques, and staying informed about emerging threats, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect against malicious intrusions.
FAQs
Is ethical hacking legal?
Yes, ethical hacking, when conducted with explicit authorization from the organization or individual who owns the IT assets, is legal. It is performed to identify and rectify vulnerabilities in cybersecurity systems and is governed by ethical guidelines and legal frameworks. Ethical hackers operate within the boundaries of the law and adhere to ethical standards to ensure that their actions do not violate any regulations or laws.
What are the benefits of penetration testing?
Penetration testing offers several benefits to organizations, including:
Identifying Vulnerabilities: Penetration testing helps uncover weaknesses and vulnerabilities in IT systems, networks, and applications before malicious attackers exploit them.
Enhancing Security Posture: By identifying and addressing vulnerabilities proactively, organizations can strengthen their cybersecurity defenses and reduce the risk of security breaches.
Compliance Requirements: Many regulatory standards and industry guidelines mandate regular penetration testing to ensure compliance with data protection regulations and security standards.
Risk Management: Penetration testing allows organizations to assess and mitigate risks associated with cyber threats, thereby minimizing the potential impact of security incidents.
Protecting Reputation: By demonstrating a commitment to cybersecurity through regular testing and vulnerability remediation, organizations can enhance their reputation and build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
How often should penetration testing be conducted?
The frequency of penetration testing depends on various factors, including the organization’s industry, regulatory requirements, and risk profile. Generally, penetration testing should be conducted:
Regularly: Organizations should perform penetration testing regularly to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
After Significant Changes: Penetration testing should be conducted after significant changes to IT systems, networks, or applications, such as system upgrades, infrastructure changes, or new software deployments.
Annually or Quarterly: Many organizations opt to conduct penetration testing annually or quarterly to ensure ongoing security resilience and compliance with regulatory standards.
What qualifications do ethical hackers need?
Ethical hackers, also known as penetration testers, require a combination of technical skills, ethical conduct, and industry certifications. Some of the qualifications and certifications commonly sought by ethical hackers include:
Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): CEH certification demonstrates proficiency in ethical hacking methodologies, tools, and techniques.
Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP): OSCP certification validates practical skills in penetration testing and offensive security techniques.
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): CISSP certification signifies expertise in cybersecurity and information security management.
Relevant Experience: Practical experience in cybersecurity, network administration, or IT security roles is highly beneficial for ethical hackers.
Can penetration testing cause downtime or disruptions?
While penetration testing is designed to uncover vulnerabilities without causing disruptions, there is a possibility of temporary downtime or disruptions during testing activities. To minimize the impact on critical business operations, penetration testers follow best practices such as:
Scheduling: Penetration tests are typically scheduled during off-peak hours to minimize disruption to business operations.
Communication: Clear communication channels are established between the testing team, organizational stakeholders, and IT personnel to coordinate testing activities and address any issues promptly.
Testing Scenarios: Test scenarios are carefully designed to prioritize critical systems and minimize the risk of unintended disruptions.
Risk Mitigation: Contingency plans are developed to address any unexpected issues or disruptions that may arise during testing, ensuring swift resolution and minimal impact on business operations.
Please check out all the computing information available at The Tech StudioX/Computing.



